Septoria on wheat in Indiana
Source:vignettes/case-study-indiana-septoria.Rmd
case-study-indiana-septoria.Rmd🎯 Goal
This vignette walks through the process of fitting Septoria tritici blotch severity data in Indiana using FraNchEstYN. We will use the example datasets bundled with the package:
-
weather_indiana: daily weather data (NASA POWER)
-
reference_indiana: digitized disease observations from Shaner & Buechley (1995)
-
management_indiana: sowing and crop management metadata from the same article.
📦 Packages
We load the FraNchEstYN package plus some helper libraries for data handling, tables, and plotting.
📥 Data loading
The three Indiana datasets are included with the package. Below we load them and preview a few rows to illustrate their structure.
| site | year | month | day | tx | tn | p | rad |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indiana | 1972 | 1 | 1 | 6.623 | -2.085 | 0.000000 | 7.45 |
| Indiana | 1972 | 1 | 2 | 2.450 | -3.212 | 3.313559 | 9.44 |
| Indiana | 1972 | 1 | 3 | 5.360 | -2.956 | 0.000000 | 8.31 |
| site | year | DOY | FINT | Disease |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indiana | 1973 | 144 | 1.00 | NA |
| Indiana | 1973 | 187 | 0.25 | NA |
| Indiana | 1974 | 141 | 1.00 | NA |
| site | crop | variety | year | sowingDOY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indiana | wheat | Generic | 1972 | 278 |
| Indiana | wheat | Generic | 1973 | 271 |
| Indiana | wheat | Generic | 1974 | 275 |
⚙️ Parameters
In FraNchEstYN, crop and disease processes are controlled by parameter sets referred to physiological and epidemiological traits.
In this vignette we are only interested in canopy light interception and disease severity, not yield formation.
For wheat: start from defaults, disable calibration of traits unrelated to light interception, and keep canopy dynamics active.
For Septoria: start from defaults, and disable calibration of yield-loss damage mechanisms. Therefore, we:
# Load default parameters for wheat
thisCropParam <- cropParameters$wheat
# Disable all calibration, then selectively re-enable light interception
thisCropParam <- set_calibration_flags(
thisCropParam,
disable = c("PartitioningMaximum",
"TbaseCrop", "TmaxCrop", "ToptCrop",
"FloweringStart",
"RadiationUseEfficiency")
)
# Load default parameters for Septoria
thisDiseaseParam <- diseaseParameters$septoria
# Disable calibration for yield-loss damage mechanisms
thisDiseaseParam <- set_calibration_flags(
thisDiseaseParam,
disable = c("RUEreducerDamage",
"LightStealerDamage",
"SenescenceAcceleratorDamage",
"AssimilateSappersDamage")
)🔧 Calibration model call
With data and parameters prepared, we can call the FraNchEstYN calibration engine. Here we fit both crop and disease model parameters simultaneously, using the Indiana datasets.
Key settings: - start_end: simulation period
(1971–1992 in this example)
- api_key: required for external API calls, but not
used here
- franchy_message: set to FALSE to silence
fun messages 😉
- iterations: number of optimization iterations
(666 here, the devil’s number 👹)
- calibration: scope of calibration ("all"
means crop + disease)
This returns a model object df containing diagnostics, parameters, and simulation outputs.
start_end <- c(1971, 1992)
api_key <- "xxx" # not used here for LLM
franchy_message <- FALSE
iterations <- 100 # the more iterations, the longer it takes but results are safer
calibration <- "all" # calibrate both crop and disease
df <- franchestyn(
weather_data = weather_indiana,
management_data = management_indiana,
reference_data = reference_indiana,
cropParameters = thisCropParam,
diseaseParameters = thisDiseaseParam,
start_end = start_end,
calibration = calibration,
apikey = api_key,
franchy_message = franchy_message,
iterations = iterations
)📊 Outputs & results
⚖️ Parameter plots
Plots show parameter ranges, defaults, and calibrated values:
-
Black / grey lines = allowable parameter
ranges
- 🔵 Blue vertical line = default value
- 🔴 Red dot = calibrated value (if calibration was enabled)
Note: crop parameters here remain at defaults (blue line only), while disease parameters include calibrated values.
df$diagnostics$calibration$plots$crop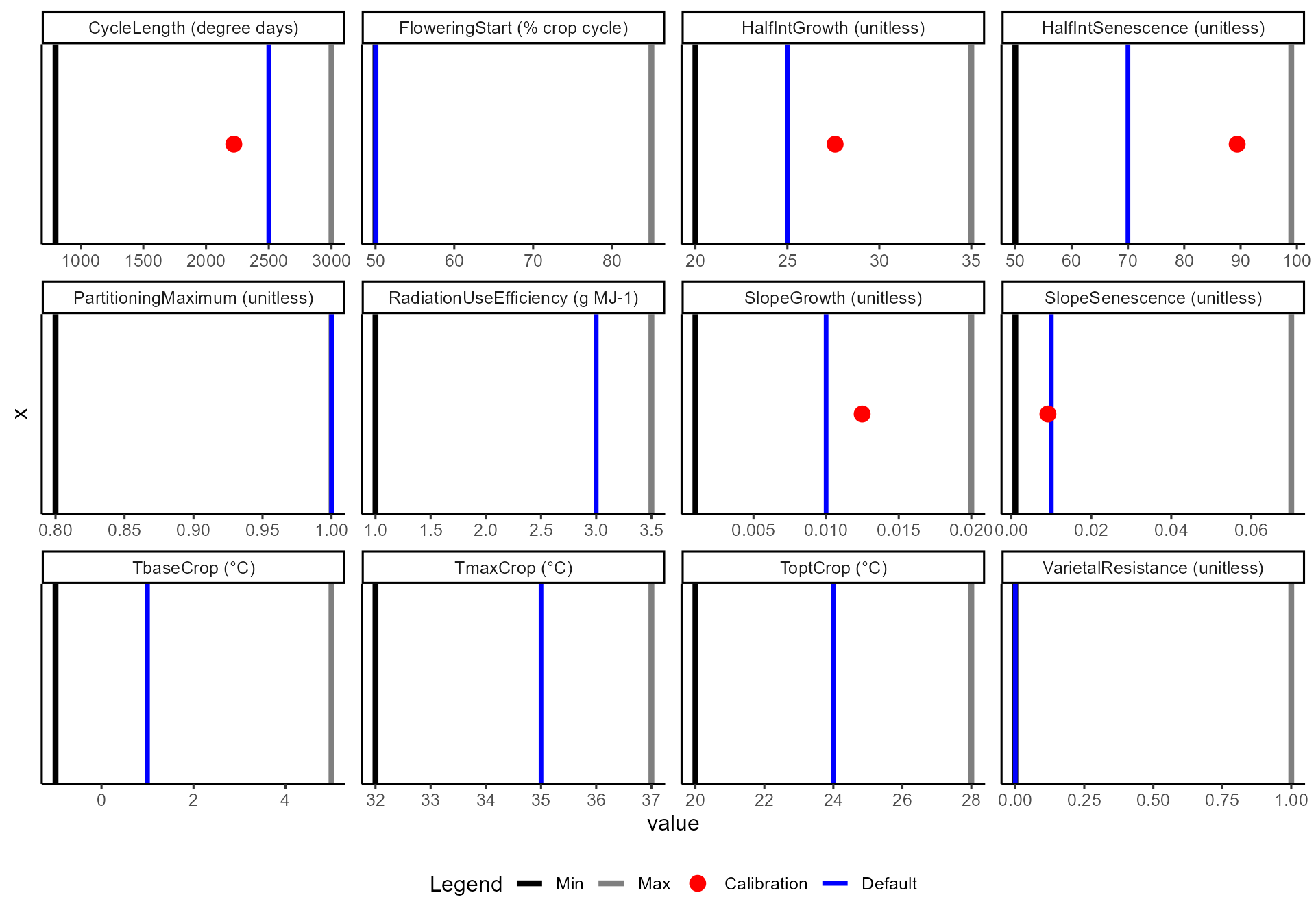
df$diagnostics$calibration$plots$disease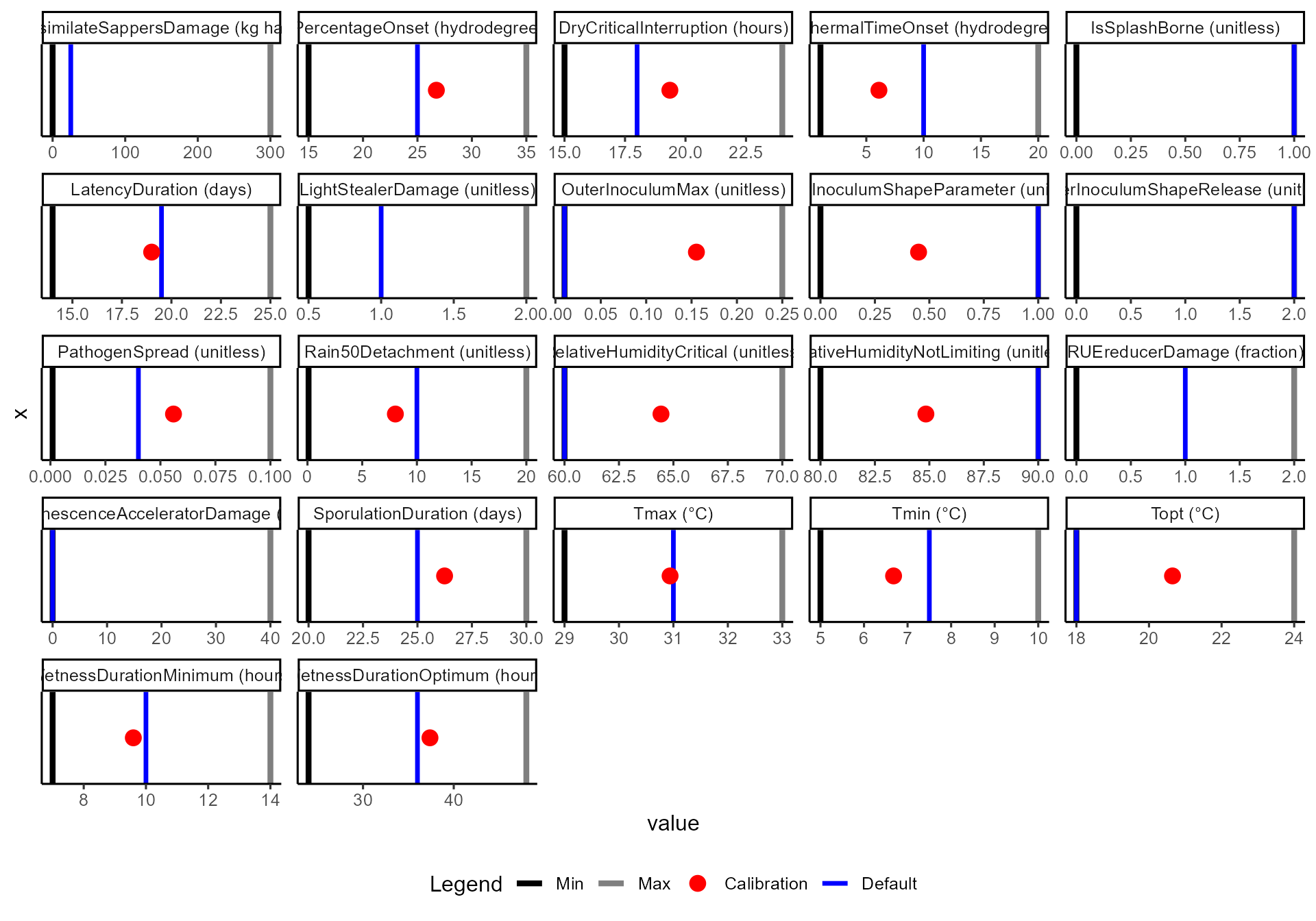
📏 Calibration metrics (Disease Severity)
We summarise calibration accuracy for disease severity across seasons using Bias, MAE, RMSE, correlation, R², and NSE.
| GrowingSeason | n | Bias | MAE | RMSE | r | R2 | NSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1972 | 8 | -0.125 | 0.127 | 0.151 | 0.960 | 0.922 | 0.752 |
| 1973 | 8 | 0.136 | 0.229 | 0.248 | 0.866 | 0.750 | 0.486 |
| 1974 | 6 | -0.139 | 0.139 | 0.157 | 0.980 | 0.960 | 0.426 |
| 1975 | 9 | 0.122 | 0.187 | 0.210 | 0.846 | 0.716 | 0.503 |
| 1976 | 3 | -0.025 | 0.148 | 0.175 | 0.842 | 0.709 | 0.371 |
| 1977 | 5 | 0.000 | 0.068 | 0.079 | 0.893 | 0.798 | 0.599 |
| 1978 | 6 | 0.105 | 0.179 | 0.197 | 0.758 | 0.575 | 0.375 |
| 1979 | 6 | 0.009 | 0.077 | 0.106 | 0.950 | 0.903 | 0.875 |
| 1980 | 8 | -0.141 | 0.141 | 0.151 | 0.984 | 0.968 | 0.701 |
| 1981 | 4 | 0.109 | 0.146 | 0.163 | 0.926 | 0.857 | 0.627 |
| 1982 | 7 | -0.005 | 0.033 | 0.038 | 0.991 | 0.982 | 0.975 |
| 1983 | 4 | 0.110 | 0.110 | 0.120 | 0.948 | 0.899 | 0.012 |
| 1984 | 2 | 0.255 | 0.255 | 0.277 | 1.000 | 1.000 | -25.046 |
| 1985 | 5 | 0.054 | 0.210 | 0.228 | 0.909 | 0.826 | 0.564 |
| 1986 | 5 | -0.287 | 0.287 | 0.363 | 0.801 | 0.642 | -1.091 |
| 1987 | 4 | -0.010 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.988 | 0.976 | 0.899 |
| 1988 | 8 | -0.115 | 0.115 | 0.172 | 0.987 | 0.973 | 0.699 |
| 1989 | 7 | -0.098 | 0.106 | 0.129 | 0.948 | 0.899 | 0.762 |
| 1990 | 5 | 0.064 | 0.209 | 0.220 | 0.868 | 0.754 | 0.475 |
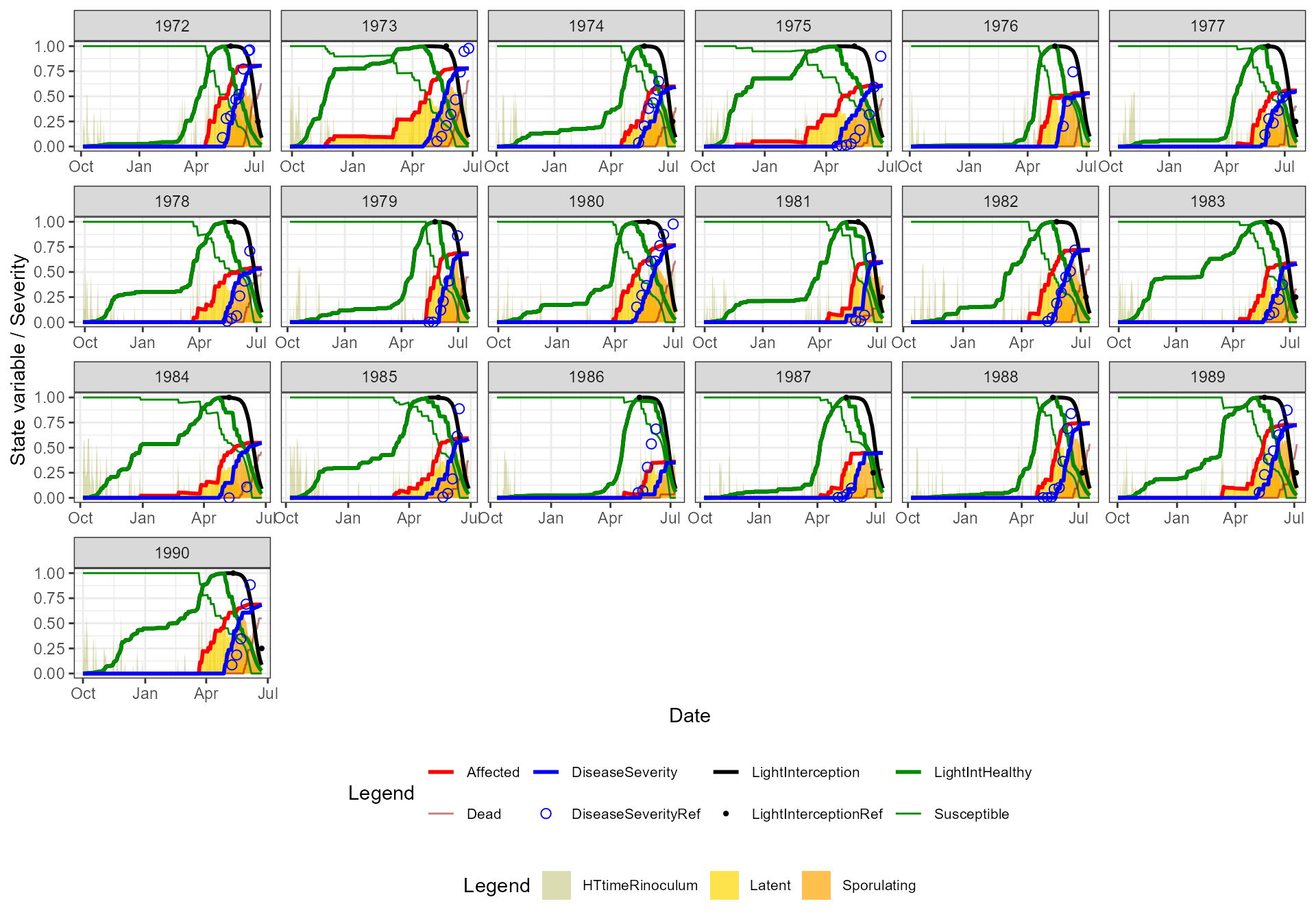
📈 Simulation outputs
🗂️ Season summary
A compact table of disease severity outcomes for each growing season: final severity, peak, timing, and area-under-curve.| GrowingSeason | Site | AveTx | AveTn | AveRHx | AveRHn | TotalPrec | TotalRad | TotalLW | AUDPC | DiseaseSeverity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1972 | Indiana | 12.414 | 4.065 | 80.582 | 48.308 | 875.504 | 3652.87 | 1917 | 3205.647 | 0.806 |
| 1973 | Indiana | 12.563 | 3.384 | 79.394 | 45.080 | 1012.792 | 3353.07 | 2160 | 3289.634 | 0.779 |
| 1974 | Indiana | 12.618 | 3.895 | 79.092 | 45.908 | 737.493 | 3922.62 | 1659 | 2163.079 | 0.593 |
| 1975 | Indiana | 13.385 | 3.172 | 78.092 | 41.581 | 569.914 | 3732.22 | 1402 | 2669.848 | 0.606 |
| 1976 | Indiana | 11.557 | 1.868 | 72.148 | 39.199 | 575.648 | 4027.05 | 1164 | 2239.769 | 0.531 |
| 1977 | Indiana | 10.699 | 1.379 | 70.966 | 39.693 | 668.018 | 3996.45 | 1527 | 2059.912 | 0.550 |
| 1978 | Indiana | 11.516 | 2.033 | 74.625 | 40.793 | 742.898 | 3871.05 | 1714 | 2372.080 | 0.537 |
| 1979 | Indiana | 12.410 | 3.371 | 77.502 | 43.676 | 817.637 | 3898.40 | 1528 | 2468.710 | 0.679 |
| 1980 | Indiana | 12.373 | 3.007 | 77.890 | 43.696 | 856.521 | 3790.90 | 1564 | 3056.156 | 0.766 |
| 1981 | Indiana | 11.367 | 1.718 | 73.992 | 40.617 | 865.298 | 3948.87 | 1820 | 1903.726 | 0.600 |
| 1982 | Indiana | 13.263 | 4.501 | 81.318 | 47.267 | 832.473 | 3699.41 | 1582 | 2941.946 | 0.720 |
| 1983 | Indiana | 11.415 | 2.658 | 75.902 | 43.926 | 832.008 | 3759.49 | 1733 | 1980.241 | 0.582 |
| 1984 | Indiana | 12.454 | 3.222 | 78.083 | 43.808 | 956.927 | 3410.67 | 1722 | 2190.895 | 0.548 |
| 1985 | Indiana | 12.504 | 3.297 | 77.475 | 44.170 | 839.796 | 3386.69 | 1613 | 1980.329 | 0.587 |
| 1986 | Indiana | 13.415 | 4.321 | 78.867 | 44.761 | 576.309 | 3787.24 | 1211 | 934.490 | 0.351 |
| 1987 | Indiana | 13.535 | 3.427 | 75.746 | 40.274 | 596.667 | 4248.61 | 1201 | 1810.863 | 0.447 |
| 1988 | Indiana | 12.894 | 3.498 | 78.834 | 43.313 | 843.670 | 4116.81 | 1687 | 2735.966 | 0.745 |
| 1989 | Indiana | 12.774 | 3.598 | 79.528 | 44.815 | 737.459 | 3684.23 | 1493 | 2677.643 | 0.722 |
| 1990 | Indiana | 13.693 | 4.171 | 79.760 | 43.890 | 766.784 | 3458.94 | 1604 | 2736.972 | 0.685 |
📝 Key take-home messages
FraNchEstYN successfully calibrated disease severity for Septoria tritici in Indiana across two decades of observations.
Crop parameters were mostly fixed (default values) — only canopy light interception was active, while disease parameters were calibrated.
The framework provides diagnostics, metrics, parameter estimates, and simulations in a consistent structure, ready for analysis or visualization.
🚀 Next steps
This vignette showed how to calibrate Septoria tritici blotch severity in Indiana using bundled datasets. From here, you might want to:
🌎 Explore other environments: replace weather_indiana, reference_indiana, and management_indiana with datasets from different sites or years.
🌾 Switch crops or pathogens: try other parameter sets available in cropParameters and diseaseParameters.
🎛️ Experiment with calibration scope:
“all” → calibrate both crop and disease models
“crop” or “disease” → focus on one component only
📊 Analyze uncertainty: increase the number of iterations or run multiple calibration replicates to assess stability of parameter estimates.
🛠️ Extend the pipeline: integrate with your own management practices or link outputs to yield-loss models. .